
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is an immersive teaching approach that engages students in real-world projects, making their learning experience more meaningful. By tackling genuine problems and complex questions, PBL brings education to life. Students work over an extended period, demonstrating their understanding and skills through tangible outputs or presentations for authentic audiences. PBL fosters deep subject knowledge, critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, and effective communication skills, igniting enthusiasm among students and teachers alike.
Extensive research demonstrates that students derive greater educational benefits from engaging in unstructured or open-ended projects, compared to highly structured ones. These projects, intentionally devoid of predetermined solutions, serve as catalysts for critical thinking, prompting students to question assumptions, consider limitations, and carefully frame the problems they seek to solve. Immersing themselves in such projects enhances students’ ability to apply acquired knowledge and skills across diverse problem-solving contexts while fostering critical and innovative thinking. Therefore, there are four compelling reasons for educators to embrace the pedagogical approach of PBL wholeheartedly.

Reasons to Embrace Project-Based Learning:
- Multidisciplinary Approach: PBL integrates multiple subjects into one cumulative project, encouraging meaningful connections across content areas;
- Building 21st-Century Skills: PBL develops critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and creativity — the Four Cs of 21st-century learning — preparing students for success in college, work, and life beyond school;
- Real-World Engagement: PBL engages students in authentic projects tied to real-world careers and experiences, fostering deeper understanding and relevance;
- Flexible Implementation: PBL adapts to various learning environments, whether in person or remote, promoting student choice, collaboration, and the development of future-ready skills.
The widespread adoption of PBL in education can be attributed to its adaptability and comprehensive methodology. Unlike traditional approaches, where projects often serve as brief and intellectually light tasks following content coverage, PBL takes a distinct approach. It positions projects as central elements that seamlessly integrate with the curricula, driving students’ comprehension and proficiency in the subject matter. To ensure effectiveness, PBL projects should embody three crucial characteristics: interdisciplinary integration, rigorous application of knowledge, and a student-centered approach.
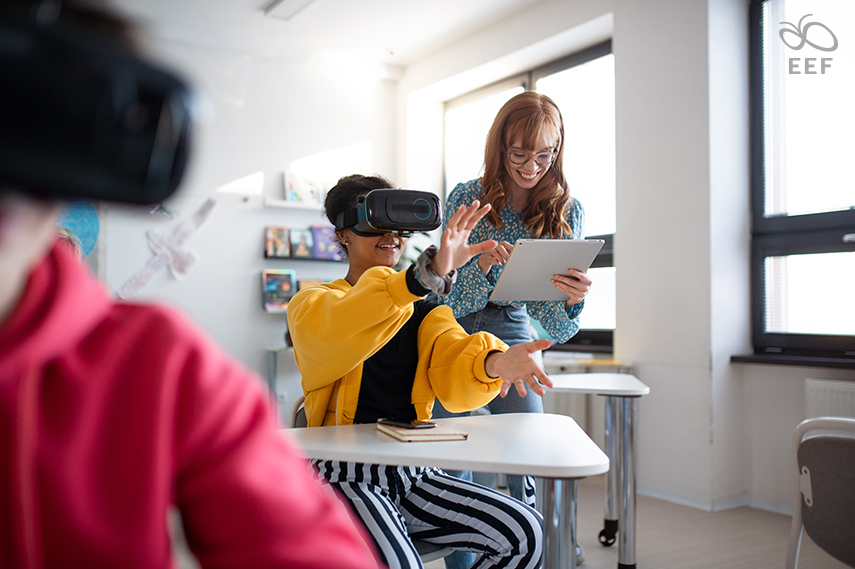

Characteristics of Project-Based Learning:
- Interdisciplinary: PBL integrates multiple subjects to tackle real-world challenges, allowing students to apply diverse knowledge and skills in problem-solving;
- Rigorous: PBL assesses students’ ability to apply academic content in new contexts through inquiry and critical thinking, resulting in the development of solutions and tangible demonstrations of knowledge;
- Student-Centered: PBL empowers students to take ownership of their learning, making independent decisions and showcasing their understanding, fostering independence and the cultivation of essential 21st-century skills.
PBL thrives on creativity and collaboration, benefitting from interdisciplinary work, technological integration, and real-world problem-solving. Projects need not be overly complex to provide valuable opportunities for students to make meaningful connections across subjects. Implementing PBL involves four essential processes, including defining problems within given constraints, generating multiple ideas, prototyping potential solutions, and testing them in authentic settings.
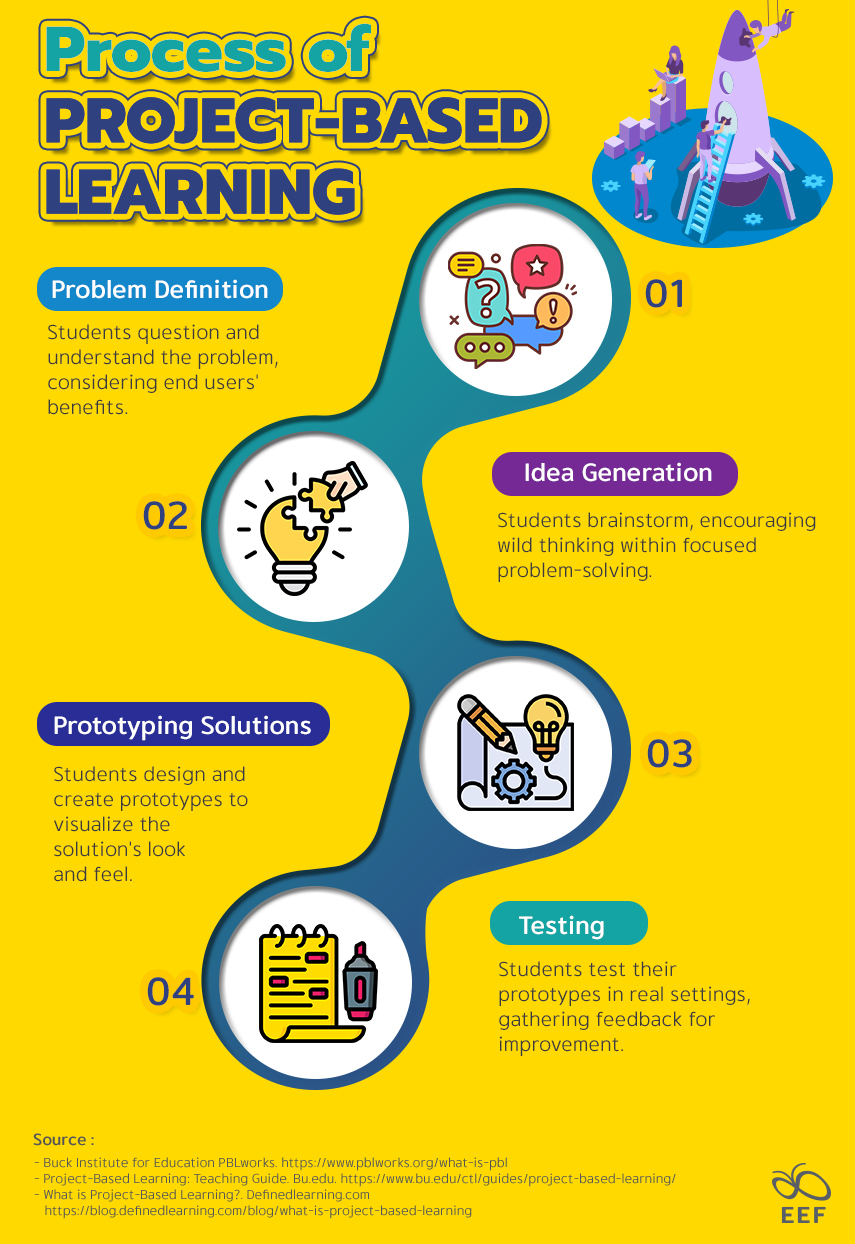
Process of Project-Based Learning
- Problem Definition: Students question and understand the problem, considering end users’ benefits.
- Idea Generation: Students brainstorm, encouraging wild thinking within focused problem-solving.
- Prototyping Solutions: Students design and create prototypes to visualize the solution’s look and feel.
- Testing: Students test their prototypes in real settings, gathering feedback for improvement.
To ensure high-quality implementation of PBL, educators are encouraged to adopt the research-informed “Gold Standard PBL” model. This comprehensive framework serves as a valuable resource for teachers, schools, and organizations seeking to enhance, evaluate, and refine their PBL practices. The primary objective of Gold Standard PBL is to facilitate students’ acquisition of essential knowledge, understanding, and success skills. The model consists of two distinct components designed to support compelling PBL experiences:

- Seven Essential Project Design Elements: A comprehensive, research-informed framework for designing a dynamic project-based learning experience.
- Challenging Problem/Question: Frame the project around a significant problem or question that provides an appropriate level of challenge.
- Sustained Inquiry: Engage students in an extended process of questioning, resource finding, and applying information.
- Authenticity: Incorporate real-world context, tasks, tools, quality standards, or personal relevance to students’ lives.
- Student Voice & Choice: Empower students to make decisions about the project, express their ideas, and determine how they work and create.
- Reflection: Encourage both students and teachers to reflect on learning, evaluate the effectiveness of project activities, address obstacles, and strategize solutions.
- Critique & Revision: Foster a culture of feedback, where students give, receive, and apply feedback to enhance their process and final products.
- Public Product: Encourage students to share and present their project work to audiences beyond the classroom.
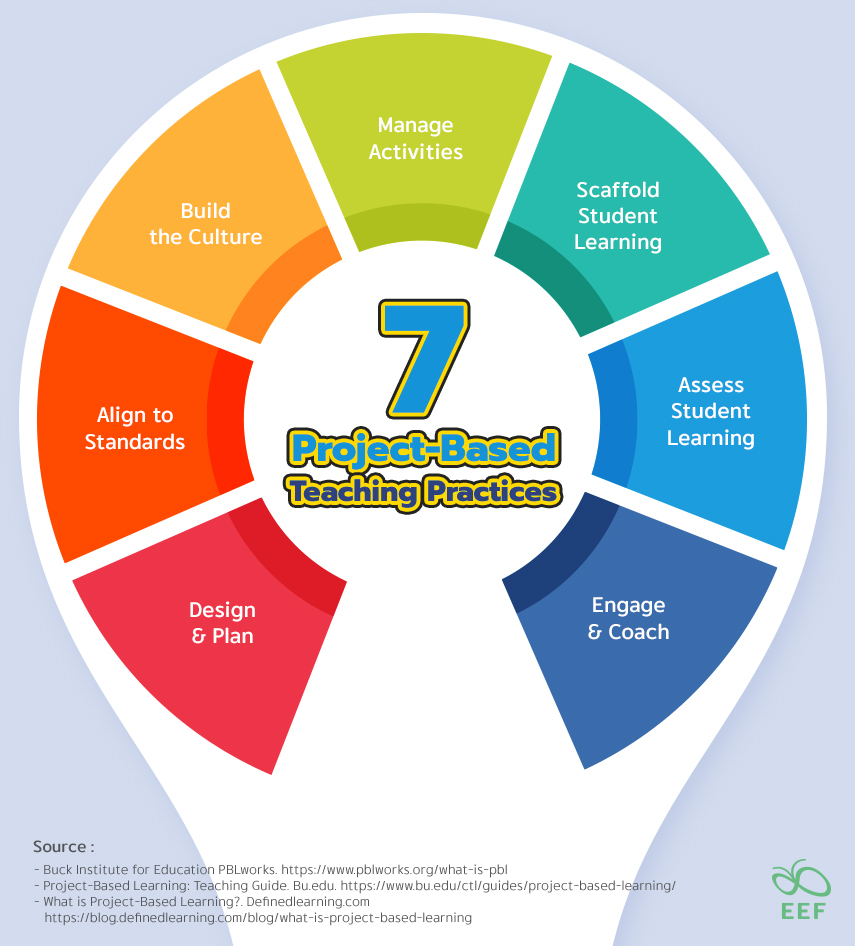
- Seven Project-Based Teaching Practices: A Comprehensive, research-informed framework for enhancing project-based teaching practices.
-
- Design & Plan: Create or adapt a project, allowing for student voice and choice, and plan its implementation from start to finish.
- Align to Standards: Ensure the project aligns with standards, integrating key knowledge and understanding from relevant subject areas.
- Build the Culture: Cultivate an environment that promotes student independence, open-ended inquiry, teamwork, and a focus on quality.
- Manage Activities: Collaborate with students to organize tasks, set deadlines, utilize resources, create products, and showcase them publicly.
- Scaffold Student Learning: Provide diverse lessons, tools, and instructional strategies to support all students in achieving project goals.
- Assess Student Learning: Utilize formative and summative assessments to measure knowledge, understanding, and success skills, including self and peer assessments.
- Engage & Coach: Actively participate in learning alongside students, identifying when support is needed and providing guidance, encouragement, and celebration.
By embracing the Gold Standard PBL model, educators can create immersive PBL experiences that foster deep learning and skill development in students. Integrating the essential project design elements and teaching practices enhances the effectiveness of PBL teaching, resulting in impactful and meaningful educational experiences.

Project-Based Learning (PBL) is a transformative teaching approach that prepares students for the future by igniting their passion for learning. Through captivating real-world projects, PBL cultivates critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity. By integrating multiple subjects and embracing interdisciplinary integration, rigorous knowledge application, and a student-centered approach, PBL equips students with essential 21st-century skills. The Gold Standard PBL model guides educators towards immersive experiences that empower students to take ownership of their learning. With each project, students embark on a journey of self-discovery, leaving a lasting impact on the world. The transformative power of PBL resonates far beyond the classroom, shaping a brighter future.
In its commitment to providing equitable and transformative education, the Equitable Education Fund (EEF) Thailand plays a crucial role in advancing the cause of PBL. By supporting schools, educators, and students across the country, the EEF ensures that all learners, regardless of their background or circumstances, have access to immersive and meaningful learning experiences. Through its initiatives, the EEF fosters the integration of PBL methodologies, empowering students to develop essential skills, critical thinking abilities, and a passion for lifelong learning. As the EEF continues to champion equitable education, it paves the way for a future where every student can thrive and reach their full potential.
Source:
- Buck Institute for Education PBLworks. https://www.pblworks.org/what-is-pbl
- Project-Based Learning: Teaching Guide. Bu.edu. https://www.bu.edu/ctl/guides/project-based-learning/
- What is Project-Based Learning? Definedlearning.com https://blog.definedlearning.com/blog/what-is-project-based-learning

