
Did you know? Student loan debt is the largest non-housing debt category in the U.S.creates financial challenges for borrowers compared to those without such debt and can result in the postponement of major purchases and life goals. Disproportionately affects black borrowers and women who often face higher debt levels and lower wages is often incurred without a clear understanding of the costs associated with a college education, poses long-term risks for taxpayers and has detrimental effects on the labor market, and contributes to income inequality, poor labor market outcomes and financial burdens for taxpayers.

Student loan debt poses a significant challenge in the United States, with borrowers collectively owing over $1.7 trillion and the average borrower burdened with nearly $30,000 owed to their lenders. Unlike other debts, student loans lack the leniency of being easily discharged through bankruptcy, thus making it arduous to evade this financial burden without complete repayment. Moreover, the enduring repercussions of student loan debt linger for many years — perhaps even decades — after graduation.
Graduating with student loan debt has long-lasting consequences for students. Beyond the stress and anxiety, it creates, this financial burden often leads to difficult choices and delays in individuals’ seminal life events.

Ways in which student loan debt can impact students’ lives:
- Career Pressure: Student loan debt leads individuals to prioritize any job over desired career paths, with 50% of graduates stating that their debts hinder career progression.
- Net Worth Reduction: Student loan debt reduces net worth, impeding major purchases and loan eligibility.
- Homeownership Delay: Student loan debt creates challenges in managing mortgage and loan payments simultaneously, leading to delays in achieving homeownership, with a 10% increase in student loan debt correlating with a 1.5% decrease in homeownership rates.
- Family Planning Setback: Student loan debt strains budgets, making it difficult to afford the costs of raising children, given that the average cost to raise a child is $233,610.
- Marital Impact: Student loan debt causes financial stress and is a leading cause of divorce in the United States.
- Credit Score Consequences: Late or missed payments on student loan debt significantly lower credit scores, with the average credit score for borrowers with student loan debt being 656, compared to the national average of 711.
- Discouraging Higher Education: Fear of accumulating substantial student loan debt deters prospective students from pursuing a college education, limiting opportunities and potentially impacting economic growth.
- Goal Postponement: Student loan debt causes significant delays in achieving life goals, be it marriage, homeownership, having children, pursuing advanced education, or career advancement.
Student loan debt can significantly delay the achievement of individuals’ seminal life goals, from marriage and homeownership, to further education and securing desired jobs. In contrast, those without student debt enjoy greater freedom to pursue their financial and personal aspirations. Beyond being a monthly obligation, student loan debt shapes major life decisions and holds implications for the economy, labor market, and wealth distribution.
Student loan debt not only poses challenges for individual students but also has broader implications for the economy. When students carry debt, their available funds for spending in the economy are reduced. As the debt-to-income ratios increase, consumer spending experiences a decline. Understanding the economic consequences of student debt is crucial for assessing its overall impact and identifying potential solutions.

Ways in which student loan debt can impact the economy at large:
- Economic Inequality: Student loan debt disproportionately affects women and Black borrowers, exacerbating income disparities, with women carrying nearly two-thirds of all student loan debt, and black female bachelor’s degree holders have a median debt of $35,000, almost twice the national median, and a median annual income of $10,000-$11,000, less than their white and male counterparts.
- Limited Access to Higher Education: The rising cost of college and student loan debt discourage individuals from pursuing higher education, with almost half of the students considering dropping out due to financial burdens.
- less than half of students believing college is worth the cost.
- less than a quarter of borrowers understand the costs of attending college before incurring debt.
- Government and Taxpayer Costs: The federal student loan program incurs significant costs for the government and taxpayers, with the estimated costs of running the program has shifted from earning $114 billion to costing $197 billion over 25 years.
- President Biden’s plan to forgive up to $20,000 of student debt is expected to cost over $400 billion in the next 30 years.
Understanding the far-reaching consequences of student loan debt is essential for individuals to grasp the true financial implications of their education. This knowledge empowers learners to make informed choices about loans and forgiveness programs, enabling them to minimize the impact on their own lives and the broader economy.
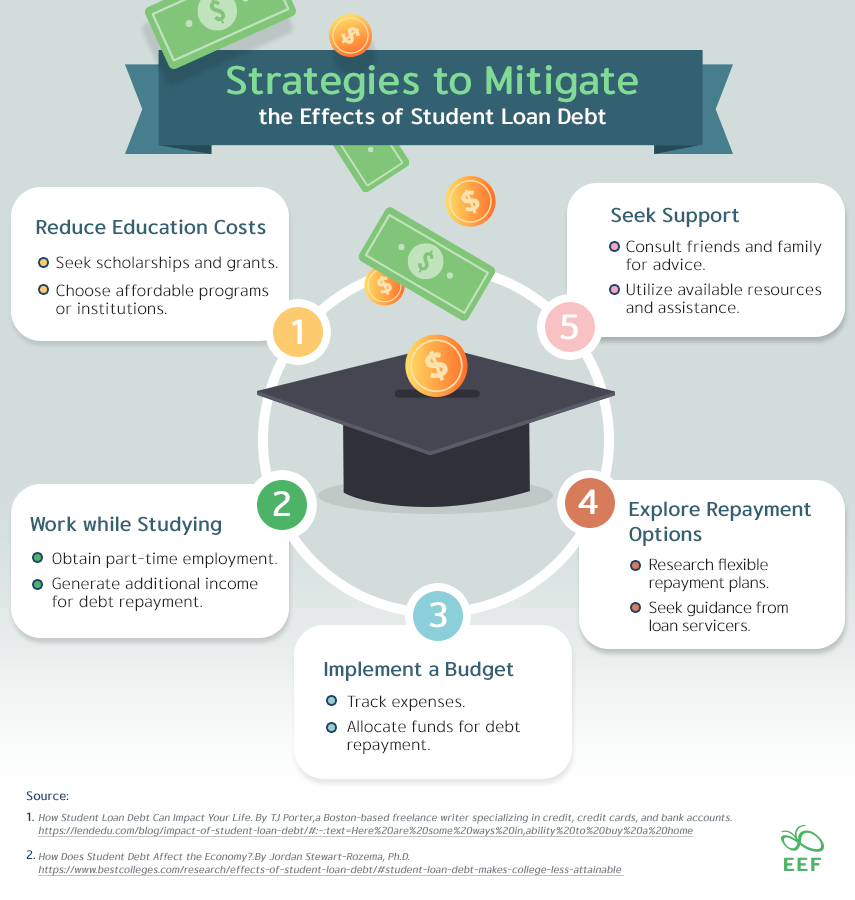
Strategies to Mitigate the Effects of Student Loan Debt:
- Reduce Education Costs:
- Seek scholarships and grants.
- Choose affordable programs or institutions.
- Work while Studying:
- Obtain part-time employment.
- Generate additional income for debt repayment.
- Implement a Budget:
- Track expenses.
- Allocate funds for debt repayment.
- Explore Repayment Options:
- Research flexible repayment plans.
- Seek guidance from loan servicers.
- Seek Support:
- Consult friends and family for advice.
- Utilize available resources and assistance.
Overcoming student loan debt is possible with strategic measures. By taking proactive steps and utilizing available resources, individuals can navigate the challenges of student loan debt and work towards a more financially secure future.

The weight of student loan debt looms heavily over the lives of individuals, shaping their decisions and impeding their aspirations. As borrowers navigate the intricate web of financial strain, delayed goals, and limited opportunities, the impact reverberates throughout the economy, perpetuating inequality and burdening taxpayers. Yet, amidst these challenges, there lies hope. By equipping students with knowledge, exploring solutions to reduce the cost of education, and fostering a culture of financial responsibility, we can alleviate the grip of student loan debt. It is high time to strive for a future where education is accessible, dreams are within reach, and the weight of debt no longer stifles the pursuit of a brighter tomorrow.
In Thailand, the Equitable Education Fund (EEF) plays a pivotal role in advancing the cause of alleviating student loan debt and fostering equitable education. By promoting access to scholarships and grants, supporting affordable educational programs, and providing financial guidance, the EEF empowers students to pursue education without incurring overwhelming debt. Through its comprehensive approach, the EEF not only addresses the immediate financial challenges but also tackles the systemic issues that contribute to student loan debt. By advocating for equitable education and empowering students with financial resources, the EEF contributes to a brighter future where education is accessible to all, regardless of their financial circumstances.
Source:
- How Student Loan Debt Can Impact Your Life. By TJ Porter, a Boston-based freelance writer specializing in credit, credit cards, and bank accounts.https://lendedu.com/blog/impact-of-student-loan-debt/#:~:text=Here%20are%20some%20ways%20in,ability%20to%20buy%20a%20home
- How Does Student Debt Affect the Economy? By Jordan Stewart-Rozema, Ph.D.https://www.bestcolleges.com/research/effects-of-student-loan-debt/#student-loan-debt-makes-college-less-attainable

