According to 2019 statistical data, out of the 20.54 million 0-25 years old population of
Thailand, 4.32 million children and teenagers have no access to quality education. Out of the majority of 2.22 million 6-14 years old (G.1-G.9) children, despite receiving the government’s free education, 430,000 children or 19.4% are still not in the school system while the rest 1.79 million children in the poor group and 1 million children in the poorest group are facing the risk of leaving the school system.

Main Objectives
Utilize information technology to improve the student fund allocation and poverty screening processes conducted by schools and teachers, and monitor the result of each student to ensure that the support money impacts equitable education and encourages participation of all sectors rather than being an immediate remedy.
How poor are Thai children who cannot afford to go to school?
From the educational inequality due to poverty in academic year 2/2020, we found that the average household income of the poorest group or equitable education fund students was reduced to 1,021 baht per month or 34 baht per day which was below the international poverty level (income lower than 1.90 USD or 60 baht per day).
The sources of income were salaries, wages, welfare from the government/private sector and farming. There were 31.8% of unemployed household members between 15-65 years old and 32% of parents holding the government welfare card. The foregoing factors may force students in the poorest group to leave the school system if they continue to go on without urgent aid and monitoring.
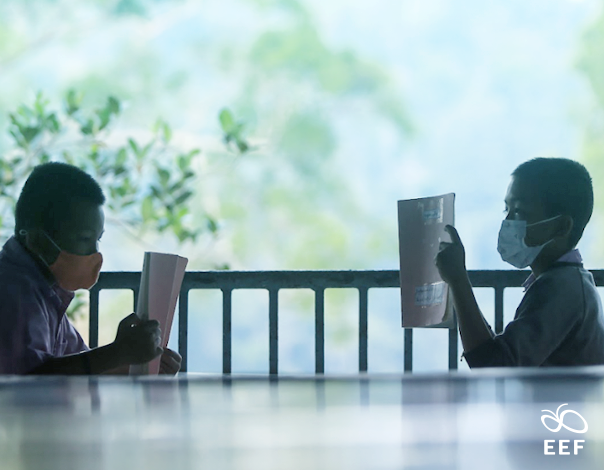

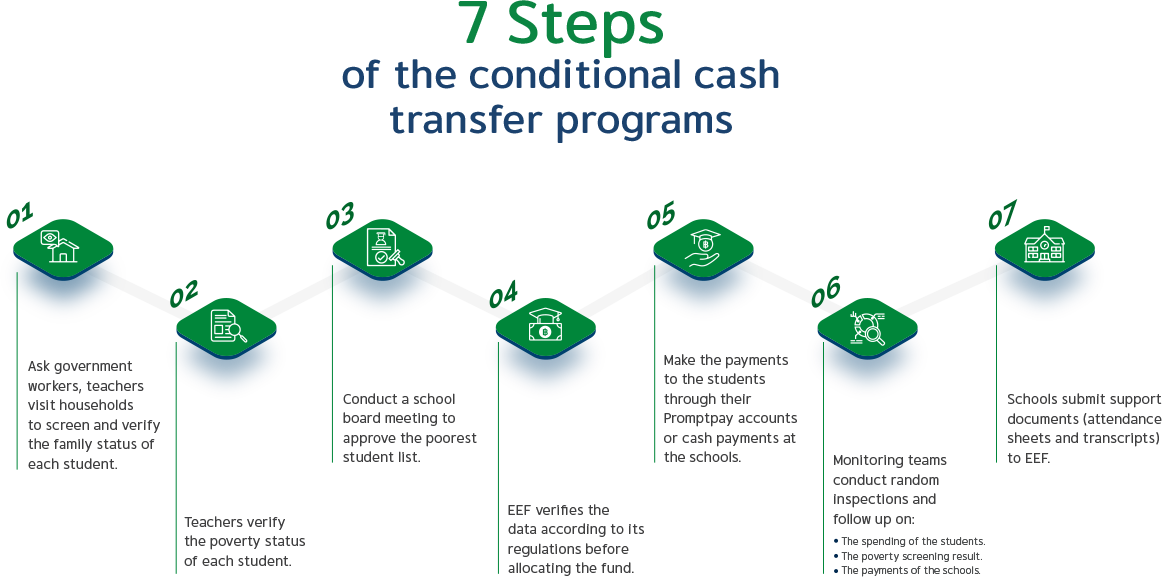
Conditional Cash Transfer Programs
How does it promote educational equality?
Indirect income screening
(Proxy Means Test: PMT)
Allocate the government budget effectively with demand-side financing to reduce educational inequality among the poorest group in the education system.


Screening, payment, monitoring, economic aid, health care, behavior and knowledge information system
Survey household status from pictures of the living conditions of the students.
Allocate the financial aid to the Promptpay accounts registered under the students’ I.D. card numbers and cash payments then report the results on an application.
Monitor the students individually such as their class attendance, roll call and growth records (weight-height) on a smartphone.
Forward aid information regarding the poor and poorest students to ensure that they will receive potential development and higher education opportunities through institutional, provincial and central big data systems.
Conditional cash transfer measures to support household expenses of the poorest students
In households with the lowest income which make up 15% of the country in the amount of 3,000 baht/person/year under the ‘Equitable Education Fund’ on the condition that the students are required to achieve 85% attendance at the minimum and the school must monitor their development closely. As of today, EEF has supported over 1.17 million students from pre-school to secondary school.

Objectives
Bring students from poverty
to the education system.
Provide conditional cash transfers.
Forward the student aid program to relevant authorities
(health, behavior and education).
Screen poverty with PMT.
Monitor the attendance and developments in the basic core education system.
Provide a higher education opportunity.
No child gets left behind.
For more information on Equitable Education Fund’s screening process,
please contact: Call Center +66 20795475 Ext. 1
or contact@eef.or.th
Others Projects